News flash: dietary surveys show a majority of Americans do NOT get their recommended daily amount of magnesium (1).
Why should you care?
Why is Magnesium So Important?
How To Tell If You’re Magnesium Deficient
What Causes Low Levels of Magnesium?
9 Magnesium Health Benefits
1. Supported Bone Strength and Density
2. Improved Energy
3. Supported Bowel Regularity
4. Help for Headaches
5. Supported Heart Health
6. Support Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
7. Better Sleep
8. Help for Muscle Cramps
9. Aid for Your Mood
The Top Natural Sources of Magnesium In Your Diet
Should You Take Magnesium Supplements?
Other Ways to Score the Benefits of Magnesium: Topically
Final Thoughts: Are You Getting Enough Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that’s responsible for over 300 different bodily functions! (2)
That means it can help you feel your best AND protect you from unwanted health conditions (1). It also happens to be one of the 7 minerals you MUST feed yourself – it doesn’t just magically appear in your body.
Let’s take a look at exactly why magnesium matters so much, how to tell if you’re deficient, the top 9 health benefits of magnesium – plus the best foods to get more in your diet.
Why is Magnesium So Important?
Magnesium is a mineral and an electrolyte just like sodium, calcium, and potassium (2). The powerful effects of magnesium help to keep your muscles and nerves functioning properly and help your body maintain adequate blood pressure and blood sugar control (1).
It’s also crucial for supporting the creation of bones, DNA, and proteins (2). Your teeth contain magnesium and almost every major organ in your body uses it, including your kidneys and heart (3).
Magnesium also plays a part in supporting digestion by helping your metabolism use energy from the foods you eat. And it supports your immune system too (4).

How To Tell If You’re Magnesium Deficient
Because magnesium is connected to so much, low magnesium levels can affect your body in a variety of different and serious ways. Here are some common symptoms:
- Muscle cramps
- Constipation
- Brain fog
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Mood imbalance
What Causes Low Levels of Magnesium?
Having a diet that is chronically low in magnesium can lead to a magnesium deficiency over time.
Besides not getting enough from your diet, low levels of magnesium can be caused by drinking too much alcohol, eating too much sugar, poor soil quality, having blood sugar or kidney issues where you’re frequently urinating, or from diarrhea (3).
The accepted RDA of magnesium depends on your age and your sex. At a minimum, men should aim for 400-420 mg of magnesium while women should shoot for 310-320 mg of magnesium daily (1).
You can add more magnesium to your diet from natural food sources, as you’ll learn more below, or use supplemental magnesium to lower your risk factors of deficiency. Here’s why you might want to do that:
9 Magnesium Health Benefits
When you give your body enough magnesium, you’ll soak up all these incredible health benefits:
1. Supported Bone Strength and Density
Magnesium plays a crucial role in converting vitamin D into a more bioavailable form so your body can better absorb and use the calcium you take in (6). Vitamin D and calcium, along with magnesium, are essential for your bone health. Vitamin D specifically helps to keep your bones strong and helps them grow, among other valuable tasks (7).
Studies show supplementing with magnesium may even suppress bone turnover in young men and postmenopausal women (6). Supplementing also led to a reduced number of fractures and greater bone mineral density in another two-year study (6).

2. Improved Energy
If you struggle with low energy levels or fatigue, boosting your magnesium intake might help. Remember that part about how magnesium is involved in over 300 bodily functions? If your magnesium levels are low, those functions might not be working optimally, which can be a stressor on your entire body.
Moreover, your energy levels are highly dependent on mitochondrial functioning. It’s ok if you don’t understand what that is, but just know that your mitochondria need magnesium to be able to produce energy (5).

3. Supported Bowel Regularity
If you struggle with regularity or have hard stools, magnesium can help in two ways. First, magnesium helps to draw more water into the bowels, which can soften stool. Second, magnesium aids in proper muscle contractions – including the contractions of your intestines that are vital to keep things moving.
This is why you’ll find many magnesium products packaged as laxatives. Please note: if you take too much magnesium, it can lead to diarrhea, which can dehydrate you (11). Use caution and check with your doctor.
4. Help for Headaches
Research from one study highlighted a connection between people who get headaches and those low in magnesium. When these participants raised their magnesium levels, they also reduced the frequency of their headaches (7).
Scientists from another body of research found supplementing with magnesium led to shorter headache episodes that were less intense and less frequent (6). And IV forms of magnesium may be useful for those experiencing an aura with their headache (6).
Despite this evidence, you should always speak with your healthcare provider for medical advice before supplementing on your own this way (7).
5. Supported Heart Health
Having low levels of magnesium can contribute to vascular calcification, which is when minerals deposit inside your blood vessel walls (6). This can spell bad news for your heart health.
But maintaining adequate magnesium levels may support your heart health. According to studies, people who consume diets rich in magnesium may have help supporting healthy blood pressure levels (7).
6. Support Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Meeting your magnesium RDA may help you maintain healthy blood sugar regulation (6). It does this in a few ways. It does this by aiding in breaking down the sugars you eat so they’re properly digested and the energy is extracted and utilized (6).
7. Better Sleep
Magnesium helps to calm certain receptors in your brain, which helps facilitate relaxation so you can unwind faster and sleep better (6).
Scientists in one study discovered supplementing with 500mg of magnesium helped participants sleep longer and increased their production of melatonin, an important hormone that helps you fall asleep and stay asleep (6).

8. Help for Muscle Cramps
Have you ever had that weird, jumpy fluttering in your eyelid? What about a charlie horse or leg cramps at night? It is believed that these can be early warning signs of low magnesium levels.
Studies have associated magnesium deficiency with muscle cramps, primarily due to the fact that you need magnesium to transport calcium and potassium across cell membranes. This process is vital for muscle contraction and nerve impulse conduction (5).
You should know, however, that there are many possible causes of leg cramps, not necessarily related to magnesium. And while studies have shown magnesium may also be able to reduce cramps from exercise, these findings weren’t strong enough to reach clinical significance (6).
More research is definitely needed in this area, but it doesn’t mean you should stop using magnesium this way if it seems to be helping.
9. Aid for Your Mood
Magnesium deficiencies may be correlated with higher rates of unstable moods (6). But evidence suggests the effects of magnesium may be useful for supporting healthy and stable moods (6).

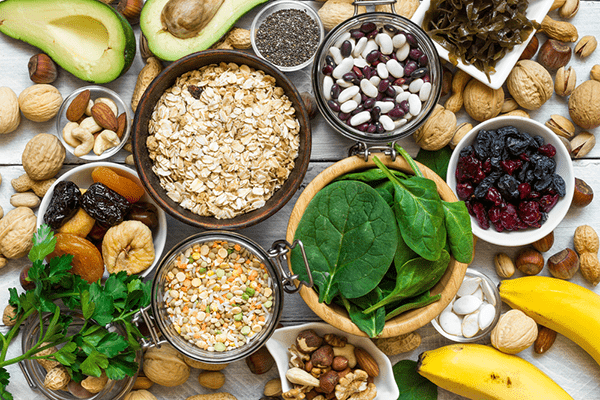
The Top Natural Sources of Magnesium In Your Diet
It’s not difficult to get your magnesium fill from whole food sources. And we’re not talking about fancy, expensive superfoods either.
You’ll find foods containing magnesium within your budget and at every grocery store. This is the safest way to up your magnesium levels and overhaul your diet without using chemically-concocted capsules or powders.
Here are some of the top magnesium-rich foods (7):
- Nuts: almonds, walnuts, pecans, cashews, brazil nuts
- Spinach (boiled)
- Black beans
- Edamame
- Chives
- Whole wheat bread
- Avocados
- Beets
- Potatoes
- Kidney beans
- Wild-caught salmon
- Bananas
- Broccoli
- Kale
- Pumpkin seeds
- Flax seeds
- Chia seeds
- Sesame seeds
- Sunflower seeds
- Dates

Should You Take Magnesium Supplements?
If you still need an additional magnesium boost, you can find easily-absorbed dietary supplements of magnesium such as magnesium aspartate, magnesium citrate, magnesium lactate, and magnesium chloride at your local vitamin shop. These are generally recognized as more bioavailable than magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate (10). Certain laxatives and antacids also contain magnesium.
While a healthy person doesn’t need to worry about overdosing magnesium from food sources, you’ll need to beware of high doses from dietary supplements. Too much could potentially interact with antibiotics, diuretics, and other medications (1). That’s why dietary sources of magnesium, such as from whole grains and leafy greens, are your best option.
But what about other ways to capture the health benefits of magnesium? Can an Epsom salt bath or lotion really provide your body with the magnesium it needs?
Other Ways to Score the Benefits of Magnesium: Topically
In addition to dietary magnesium supplements and getting magnesium from the foods you eat, there are also claims that your body can absorb magnesium from topical solutions. These include magnesium sprays, lotions, flakes, and Epsom salt baths.
While these solutions may help relieve muscle cramps or combat fatigue homeopathically, there just isn’t enough scientific research or evidence to confirm their effectiveness for sure (8). That’s why you should reach for magnesium-rich foods as often as you can. But if those aren’t quite doing the trick, you might want to try these topical methods and see how you feel.
Final Thoughts: Are You Getting Enough Magnesium?
The long-term repercussions of being magnesium deficient are nothing to mess around with. People most at risk for low magnesium levels include older adults, teenage girls, and people with kidney problems, gastrointestinal conditions, type 2 diabetes, or alcohol dependence.
Remember, you don’t have to wait until you notice fatigue, headaches, or any of the other signs of a magnesium deficiency to add more to your diet. Now that you know why dietary magnesium intake is so critical for your body to function at its best, try to eat more foods containing this essential mineral starting today.






